 |
|
Before gold was given out, it had to be carefully weighed because it was so valuable.
When the day came to an end, the gold a person had used (if there was any left over) was again weighed to make sure that none
was lost or stolen. A furnace stood in the corner of many workshops, which was used to melt the gold. Jewellers worked
with valuable stones, which they set into bracelets and rings, or made them into beads for necklaces. Lots of stones were
used to make beads for necklaces that the Egyptians wore. Blue lapis-lazuli and red carnelian stones were used to make necklaces.
Some other stones that might have been used are clear rock-crystal, crimson garnet and stones that have shades of purple.
An ornament worn on the chest took the chape of a bird with its wings spread out (it was only worn by the pharaoh). There
are many other crafts done in Egypt such as pottery making, crafting with copper and bronze, leather work, working with papyrus
paper that scribes wrote on and basket work.
|
|
 |
|
Some of the Types of Craft Workers:
- builders
- potters
- glass-blowers
- stonemasons
- carpenters
|
|
 |
|
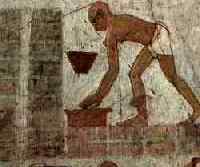
Some materials builders used were
mud, stone, motar and wood. Ancient Egyptian builders mixed mud with straws, which surprisingly resulted in stong bricks.
Each brick was usually 45 to 30 cm in length and 20 to 15 cm in width. A modern mud brick maker can produce between 1000
and 2000 bricks a day. People rarely lived in stone buildings. Most stone used to build buildings were limestone, and
granite, one of the hardest rocks, was used rarely. The great pyramids were originally covered with it. Little wood was available and therefore it was
used sparingly. Doors, shutters and upper floors were made of it. When a building was abandoned, all wooden and stone parts
such as doors, lintels etc. were removed to be reused somewhere else.
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
|

